|
|
CASO CLINICO
Acute Aortic Dissection
Pubblicato da: Dott. Roberto Mendia il 21/07/2013
email: info@cardiovascularprevention.com
A.C. female , 64 y.o.
Acute Aortic Dissection : Trans Thoracic Echocardiographyc and pleuro-polmonary sonographic examination
Mild pericardial effusion.Proximal Type II aortic dissection. Mild pericardial effusion.
Intimal flap is clearly visible.
Left pleuro-pulmonary sonographic examination show large left pleural effusion and a wide area of inferior pulmonary consolidation(atelectasis).
Careful examination shows a corpusculated component of effusion(light hematic effusion), sign of incipient aortic rupture.
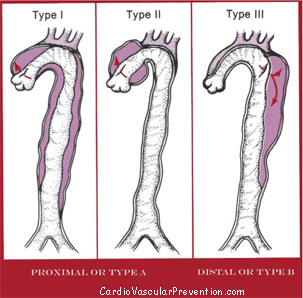
Aortic dissection. Schematic view( From Braunwald Heart disease vEd. Modifyed)
|
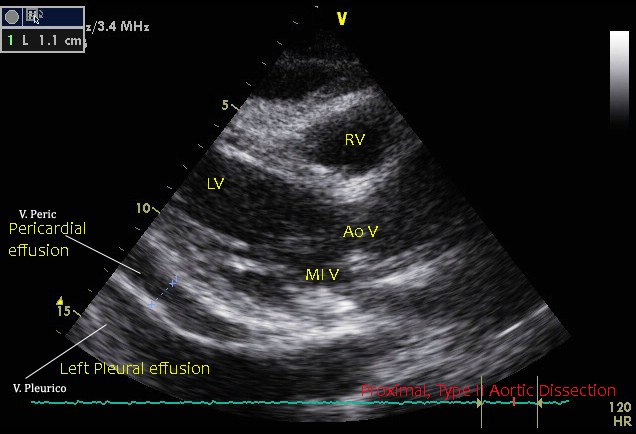
Trans Thoracic Echocardiographyc , 2D examination.- Left Parasternal, Long axis view.RV: Right Ventricle, LV: Left Ventricle; AoV: Aortic Valve; MI V: Mitral Valve.
|
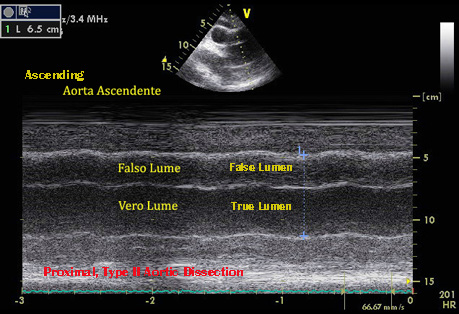
Trans Thoracic Echocardiographyc , M Mode examination - Left Parasternal, Long axis view.True Lumen and false lumen are separated by intimal flap
|
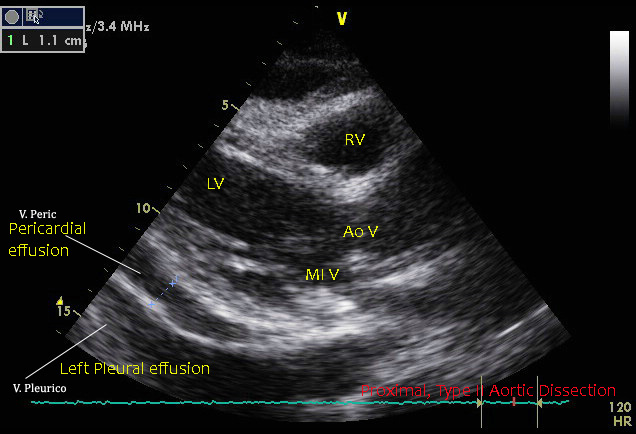
Trans Thoracic Echocardiographyc , 2D examination.- Left Parasternal, Long axis view.RV: Right Ventricle, LV: Left Ventricle; AoV: Aortic Valve; MI V: Mitral Valve.
|
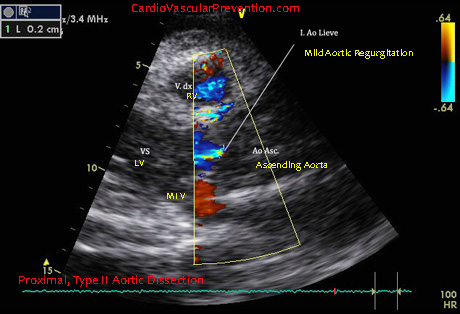
Trans Thoracic Echocardiographyc , 2D examination - Left Parasternal, Long axis view. Mild aortic effusion. RV: Right Ventricle, LV: Left Ventricle; AoV: Aortic Valve; MI V: Mitral Valve.
|
COMMENTI
|
Al momento non sono presenti commenti per questo caso clinico.
|
|
|